If Delta Lake Uses Immutable Files, How Do UPDATE, DELETE, and MERGE Work?
Listen and Watch here One of the most common questions data engineers ask is: if Delta Lake stores data in immutable Parquet files, how can it support operations like UPDATE , DELETE , and MERGE ? The answer lies in Delta Lake’s transaction log and its clever file rewrite mechanism. 🔍 Immutable Files in Delta Lake Delta Lake stores data in Parquet files, which are immutable by design. This immutability ensures consistency and prevents accidental corruption. But immutability doesn’t mean data can’t change — it means changes are handled by creating new versions of files rather than editing them in place. ⚡ How UPDATE Works When you run an UPDATE statement, Delta Lake: Identifies the files containing rows that match the update condition. Reads those files and applies the update logic. Writes out new Parquet files with the updated rows. Marks the old files as removed in the transaction log. UPDATE people SET age = age + 1 WHERE country = 'India'; Result: ...




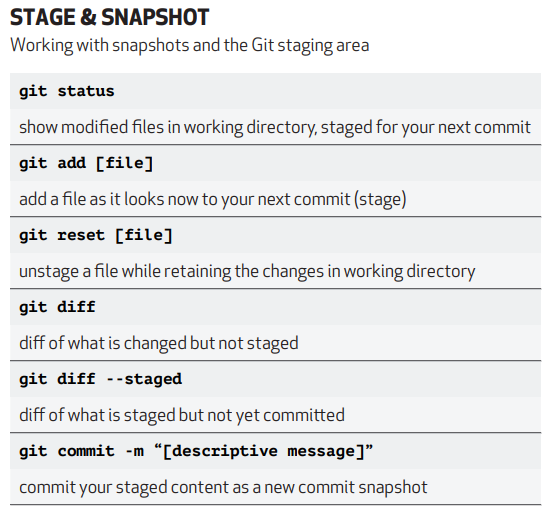
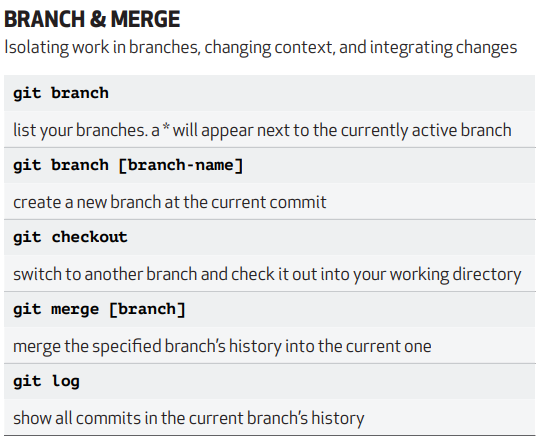

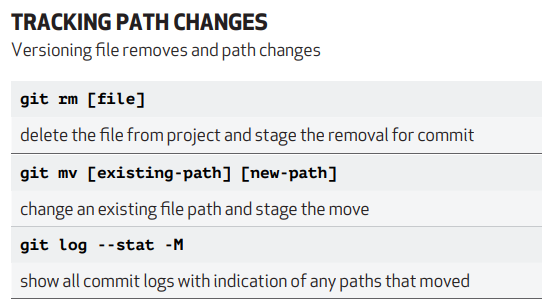





good insight about git commnad
ReplyDeleteInsightful and very helpful.
ReplyDeleteAppreciate your feedback, always happy to help
Delete